A quick guide to Smart Maintenance features vs. ISO 55000
Technology changes fast; this article is dated July 2025.
Introduction
Smart Maintenance technologies promise transformation but often stall at the pilot stage, despite significant potential for industrial companies in Asia to enhance maintenance, reduce costs, and boost operational efficiency. Historically overlooked, maintenance now faces new pressures from evolving regulations, competition, and technology. How can organizations align technology with improvement needs? This article offers a concise guide to key smart maintenance features, aligned with ISO 55000’s asset management framework, to help industrial CIOs, plant managers, and stakeholders make informed decisions.
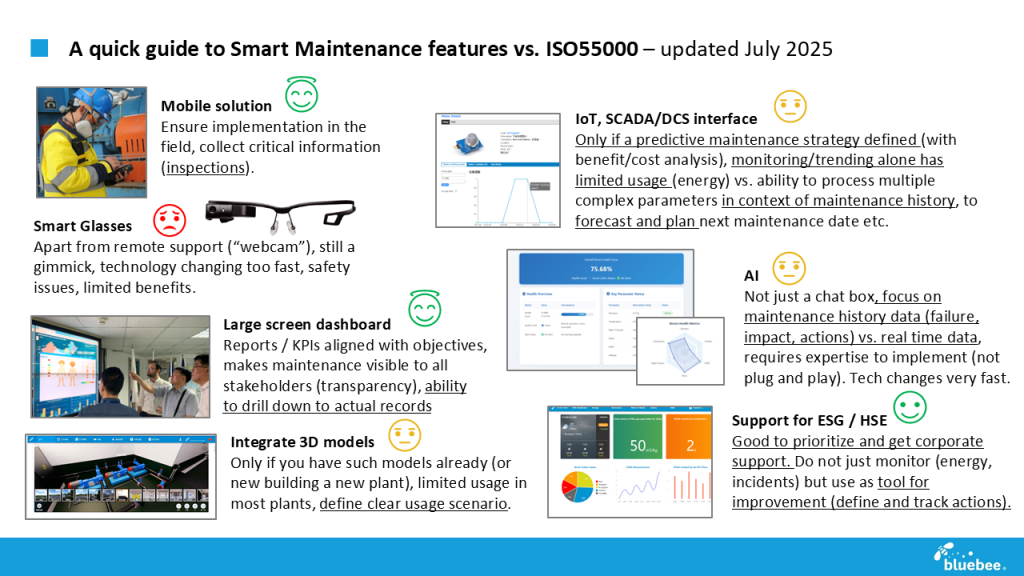
Mobile solution: Implementing the management loop, empowering the frontline
●
ISO 55000 emphasizes field implementation of asset management strategies, with technicians as critical stakeholders in the “ISO 55000 loop.” Mobile apps must support work execution, ensure traceability, and collect data for continuous improvement, with inspections playing a pivotal role.
●
Most apps, however, are not worker-friendly, focusing on time and cost reporting rather than action-level inspection data. Prioritize easy input for failures, inspection records, and meter readings via asset tag scans, photos, and quick-select features.
IoT and SCADA/DCS integration: From data deluge to precise prediction
●
ISO 55000 prioritizes maintenance strategies that optimize asset performance. Integrating IoT or SCADA/DCS with CMMS often overwhelms databases with excessive alarms and parameters, triggering work orders with little value. Instead, IoT data must align with a defined maintenance strategy, using benefit/cost analysis to enable predictive planning rather than reactive corrections.
●
Many systems treat anomalies as triggers for corrective maintenance, not predictive. Effective integration leverages IoT for trending and forecasting, incorporating maintenance history to meet ISO 55000’s focus on long-term optimization.
AI-driven insights: Historical data understands the future better than real-time data
●
AI can enhance ISO 55000’s strategic goals by analyzing maintenance and failure history to deliver actionable insights, but it’s not plug-and-play. Expertise is critical, as Prognostics and Health Management (PHM) research highlights the superior value of historical records over real-time data.
●
Many AI tools overemphasize real-time IoT data, promising instant predictive maintenance. Prioritize systems that integrate maintenance history and inspection results to forecast failures and plan interventions, avoiding low-value chatbots to align with ISO 55000’s focus on long-term optimization.
ESG/HSE support: Beyond reporting, driving corrective actions
●
ISO 55000 encourages aligning maintenance with broader organizational objectives, including sustainability. Smart tools must go beyond monitoring energy or compliance metrics, enabling traceable corrective actions to drive improvement.
●
Many solutions stop at tracking consumption or recording incidents for reports. Prioritize tools that offer actionable ESG/HSE tracking, ensuring proof of compliance and supporting ISO 55000’s governance and sustainability goals.
Large screen dashboards: Making maintenance visible and manageable
●
Transparency is central to ISO 55000. Dashboards with real-time KPIs and drill-down capabilities make maintenance visible to stakeholders, but many rely on static exports, limiting insight.
●
Choose dashboards that align with strategic objectives, allow access to specific records, and avoid superficial displays that obscure data, ensuring ISO 55000’s transparency standards are met.
3D models: BIM is not a showpiece, utility over showmanship
●
Vendors often promote 3D user interfaces for real-time data, which are visually striking but impractical for operations and maintenance (O&M) teams, offering minimal value. Traditional BIM stakeholders frequently lack expertise in adapting models for maintenance purposes.
●
Only pursue BIM for maintenance if a model is already planned, such as for new construction. Engage early to treat it as a tool for handing over construction data to maintenance, defining clear usage scenarios that align with ISO 55000’s strategic asset management focus.
Smart glasses: The tech is cool, but invest cautiously
●
In practice, smart glasses are primarily used for remote support, functioning as head-mounted webcams, with minimal benefits beyond this role. Rapidly evolving technology, often obsolete within six months, and safety concerns render them impractical for broad adoption.
●
Given these limitations, monitor market developments and test sparingly if budget permits, but focus on technologies that better align with ISO 55000’s strategic asset management goals.
Strategic leadership enables steady and long-term Smart O&M
By leveraging ISO 55000, organizations can strategically select and implement smart maintenance tools that align with business needs. This approach ensures compliance, promotes sustainability (e.g., ESG/HSE goals), and maximizes long-term value, driving operational excellence. Thoughtful adoption of these solutions empowers industrial organizations to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving landscape.
This article is based on a presentation given by Bruno Lhopiteau, CEO of Bluebee Tech and Siveco China, on the topic of “Transforming your Plant with Smart Maintenance – Practical Guidelines & Demo” in July 2025.
Siveco China, founded in 2004, is one of the pioneers in Asset Management and Maintenance consulting and CMMS/EAM implementation in the country. Bluebee Technologies, a spin-off of Siveco China R&D Center, designs innovative yet practical Smart O&M solutions known as bluebee®. bluebee® supports Industrial Risk Management, Asset Management and ESG / HSE.




